[ad_1]
By now, you’ve possible seen the bulletins concerning the March 2024 Core Replace. This main replace will roll out over the whole month and goals to scale back “unhelpful” content material by 40%.
Curiously, Google also updated its spam policies to name out some new varieties of spam it targets.
Let’s delve into what precisely modified in Google’s spam insurance policies and what these adjustments imply for the way forward for search engine optimisation.
What’s Modified In The Spam Insurance policies?
Google has launched two new sections to its spam insurance policies: “expired area abuse” and “web site repute abuse.”
It additionally overhauled an current part beforehand referred to as “spammy auto-generated content material,” now referred to as “scaled content material abuse.”
What I recognize about these updates is that all of them include real-world examples throughout the spam insurance policies, and it’s not tough to determine what conditions these adjustments are stemming from.
All these three subjects are fairly juicy, so let’s soar into every in additional element.
Expired Area Abuse
Google has added “expired area abuse” as a brand new kind of spam it targets. Some folks might know this tactic as area squatting.
Google defines it as:
The place an expired area title is bought and repurposed primarily to control search rankings by internet hosting content material that gives little to no worth to customers.
Google beforehand denied that purchasing expired domains has any benefit. However that’s not the case, or the search engine wouldn’t be taking extra steps to fight it.
So, how did folks manipulate search outcomes by shopping for expired domains?
One technique includes buying an expired area in a associated area of interest with priceless backlinks to hurry up the method of constructing authority. Individuals who do that will redirect pages from the expired area to the related pages on the location for which they’re making an attempt to construct authority.
Some will purchase an expired area and proceed constructing the location, capitalizing on the authority others have constructed for it. There isn’t something inherently incorrect with this.
Google appears involved with penalizing websites that use spammy ways to construct authority, akin to producing AI content material at scale or promoting hyperlinks or visitor posts.
A fast search on Google for [buy expired domains] on Reddit reveals that it is a extra widespread follow than folks notice.
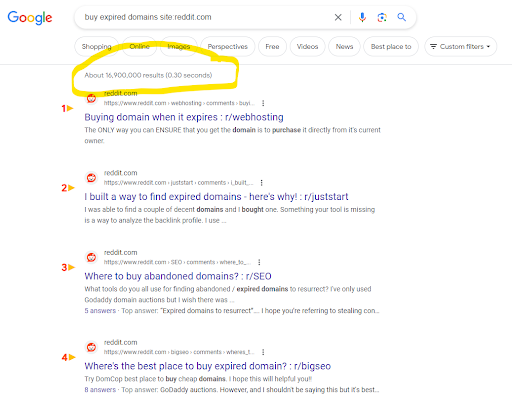 Screenshot from seek for [buy expired domains site:reddit.com], Google, March 2024
Screenshot from seek for [buy expired domains site:reddit.com], Google, March 2024Google offers a couple of examples of expired area abuse:
- Affiliate content material on a web site beforehand utilized by a authorities company.
- Industrial medical merchandise being bought on a web site beforehand utilized by a non-profit medical charity.
- On line casino-related content material on a former elementary faculty web site.
These are egregious examples, and I couldn’t discover the real-world situation for any of them. If of any, be at liberty to depart them within the feedback.
A problem I can recall is The Hairpin case, which had a viral second earlier this yr due to Wired’s Confessions of an AI Clickbait Kingpin.
The Hairpin was a once-beloved, women-run indie web site. It ceased publication in 2018, and the area expired in 2023.
It was promptly bought by a Serbian DJ named Nebojsa Vujinovic, who then reworked the location into an AI-generated content material farm.
Some unique content material stays with new formatting, however the writer names have been changed with male names with none on-line presence.
It’s a reasonably apparent instance of expired area abuse, and Vujinovic even admitted to Wired that he purchased the area for its authority and repute.
Fortunately, The Hairpin web site was lately de-indexed; might its unique content material RIP.
![Screenshot from Google for [site:thehairpin.com], March 2024](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/the-hairpin-deindexed.png) Screenshot from seek for [site:thehairpin.com], Google, March 2024
Screenshot from seek for [site:thehairpin.com], Google, March 2024Web site Status Abuse
The opposite kind of spam added to Google’s spam insurance policies is web site repute abuse, additionally generally referred to as Parasite search engine optimisation or pSEO.
Google defines it as:
When third-party pages are printed with little or no first-party oversight or involvement, the place the aim is to control search rankings by making the most of the first-party web site’s rating indicators.
Of specific curiosity, it specifies that this consists of:
Sponsored, promoting, accomplice, or third-party pages which can be sometimes unbiased of a bunch web site’s most important goal or produced with out shut oversight or involvement of the host web site, and supply little to no worth to customers.
Google goes on to offer some examples. My private favourite:
A sports activities web site internet hosting a web page written by a third-party about “exercise dietary supplements evaluations,” the place the sports activities web site’s editorial workers had little to no involvement within the content material and the principle goal of internet hosting the web page is to control search rankings.
That is possible in response to Sports Illustrated’s AI scandal that went viral in November 2023. Futurism found that there have been AI-generated product evaluations written in Sports activities Illustrated with faux authors.
It blew the whistle on these nonsensical evaluations that mentioned issues like, “Volleyball is usually a little difficult to get into, particularly with out an precise ball to follow with.”
The Area Group (the corporate that owned the publishing rights to Sports activities Illustrated on the time) issued a statement that the articles have been created by a accomplice referred to as AdVon, which runs ecommerce product evaluations throughout a lot of its net properties, and that it was unaware that AdVon was utilizing AI-generated content material.
Google’s spam coverage replace basically flags this as a web site repute abuse. The Area Group and different giant publishers who interact in such follow want to finish these partnerships or de-index these pages, or they’ll be penalized.
Plus, the dearth of oversight or involvement within the accomplice content material technique is irrelevant if it’s in your area.
One other instance Google gave that sparked dialogue within the search engine optimisation group is:
A information web site internet hosting coupons supplied by a third-party with little to no oversight or involvement from the internet hosting web site, and the place the principle goal is to control search rankings.
Gannett’s USA At this time has a surprisingly sturdy coupon community hosted on a subdomain. I believe it isn’t the one one, however it could be the largest.
It’ll be attention-grabbing to see what it does in response to being referred to as out. Clearly, Google is making an attempt to get information publishers to remain of their lane as a result of it’s onerous to argue that coupons present no worth to customers.
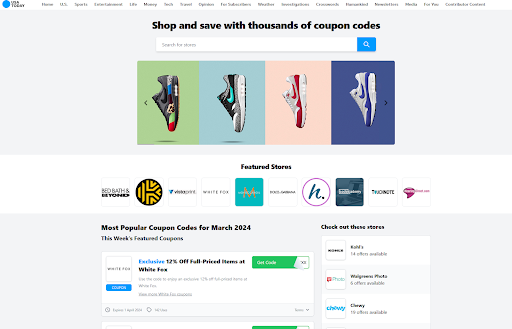 Screenshot of USA At this time, March 2024
Screenshot of USA At this time, March 2024Google’s web site repute abuse penalties aren’t going into impact till Might 2024, so publishers have time to get their geese in a row and regulate their methods. They need to determine whether or not to de-index pages that might violate this coverage, finish partnerships, or (I suppose) take their possibilities and forge forward.
Within the spam insurance policies, Google hyperlinks to a web page explaining learn how to de-index content material.
Scaled Content material Abuse
The final space of change in Google’s spam insurance policies is rebranding “spammy mechanically generated content material” as “scaled content material abuse” and broadening its definition with examples.
In a earlier model of the spam insurance policies in January 2024, Google defines “spammy mechanically generated content material” as:
Content material that’s been generated programmatically with out producing something unique or including ample worth; as a substitute it’s been generated for the aim of manipulating search rankings and never serving to customers.
At this time, Google has rebranded this to “scaled content material abuse” and defines it as:
When many pages are generated for the first goal of manipulating search rankings and never serving to customers. This abusive follow is often centered on creating giant quantities of unoriginal content material that gives little to no worth to customers, irrespective of the way it’s created.
The previous definition particularly targets programmatic content material, whereas this new definition says it doesn’t matter how the content material is generated.
What issues is that the content material is unoriginal and doesn’t add worth, no matter the way it’s created – programmatically, AI-generated, or low-quality human-created.
The outdated model additionally comprises six examples, all of which begin with “textual content,” indicating that they’re concentrating on phrases on the web page. On this new model, codecs aren’t talked about in any respect.
The implication is that scaled content material abuse may additionally contain a broader array of codecs like pictures or movies.
Within the scaled content material abuse definition, Google offers these 5 examples:
- Utilizing generative AI instruments or different comparable instruments to generate many pages with out including worth for customers.
- Scraping feeds, search outcomes, or different content material to generate many pages (together with by way of automated transformations like synonymizing, translating, or different obfuscation strategies), the place little worth is supplied to customers.
- Stitching or combining content material from totally different webpages with out including worth.
- Creating a number of websites with the intent of hiding the scaled nature of the content material.
- Creating many pages the place the content material makes little or no sense to a reader however comprises search key phrases.
An instance: In August 2023, Time exposed an pressing care clinic referred to as Nao Medical, which was discovered flooding the web with nonsensical AI-generated posts about subjects like what occurs when unicorns devour ketamine or a medical situation referred to as “Derek Jeter Herpes Tree.”
These pages are not reside and have seemingly been faraway from the Web Archive.
Conclusion
Of every little thing that’s on this March 2024 core replace, I’m most inquisitive about what falls beneath scaled content material abuse.
Loads of giant manufacturers are using programmatic templates to construct out content material on their higher-value transactional pages. Take any ticketing market web site, for instance.
The beneath web page for Colorado Rapids tickets has all the acceptable content material for buying tickets.
However additional down the web page, there may be lower-quality programmatic content material, presumably to attempt to rank for extra associated key phrases.
So, would a web page like this get dinged although it’s a transactional web page, and this programmatic content material isn’t the main target?
 Screenshot from Stubhub, March 2024
Screenshot from Stubhub, March 2024Clearly, a number of content material publishers have scaled their content material technique using a big workers of freelance writers who crank out day by day articles to rank in Google Information and High Tales.
The standard of this content material varies significantly, however most of it will get fairly repetitive. Will that get penalized? It appears unlikely.
Time will inform what occurs, however I’m undoubtedly able to see some shake-ups.
Extra sources:
Featured Picture: YoloStock/Shutterstock
[ad_2]
accepting guest postscontact us

📰 Karthic is a seasoned journalist and skilled writer passionate about uncovering compelling stories. With a knack for storytelling and a commitment to integrity, he covers diverse topics, from current affairs to human interest stories. Karthic’s writing is known for its engaging style and meticulous research. Connect with him for insightful perspectives on pressing issues! 📝
